Download our free SNMP White Paper. Featuring SNMP Expert Marshall DenHartog.
This guidebook has been created to give you the information you need to successfully implement SNMP-based alarm monitoring in your network.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayLet's examine the communication between managers and agents. Basic serial telemetry protocols, like TBOS, are byte-oriented, with a single byte exchanged to communicate. Expanded serial telemetry protocols, like TABS, are packet oriented with packets of bytes exchanged to communicate. The packets contain header, data and checksum bytes. SNMP is also packet oriented with the following SNMP v1 packets (Protocol Data Units or PDUs) used to communicate:
The manager sends a Get or GetNext to read a variable or variables and the agent's response contains the requested information if managed. The manager sends a Set to change a variable or variables and the agent's response confirms the change if allowed. The agent sends a Trap when a specific event occurs.
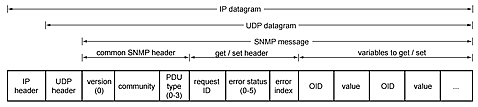
The above illustration shows the packet formats. Each variable binding contains an identifier, a type and a value (if a Set or GetResponse). The agent checks each identifier against its MIB to determine whether the object is managed and changeable (if processing a Set). The manager uses its MIB to display the readable name of the variable and sometimes interpret its value.
Essential SNMP: What is UDP?UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is the IP transport layer protocol that supports SNMP messages. Unlike TCP, UDP is a connectionless protocol. A UDP host places messages on the network without first establishing a connection with the recipient. UDP does not guarantee message delivery, but it's a lightweight protocol that can transport a large number of status messages without using too many network resources. |